-
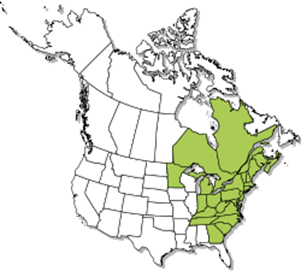
Shrews
are one of the less common rodents that we will receive service requests for. Customers may call because of damage in mulch
beds or they have misidentified the activity as moles.
Shrews may get into crawl spaces and leave droppings behind.
-
Remember
to use the information provided by the customer as a starting point for inspection. This may come from direct communication with the customer or the
notes from client service detailed in the work order/proposal.
-
On initial
inspection start by walking around the exterior of the home. Check mulch beds for tunneling and potential entry
points into the structure around the foundation.
-
Tunnels created
by shrews will be cigar-shaped with openings, but shrews will commonly occupy
mole tunnels as well.
-
Shrew
droppings are curved and tapered and rough-textured because of the insect
fragments in them. Some shrews, such as the short-tailed shrew, produce
“corkscrew-” shaped droppings.

Shrew Droppings in Crawl Space

Shrew Tunnels