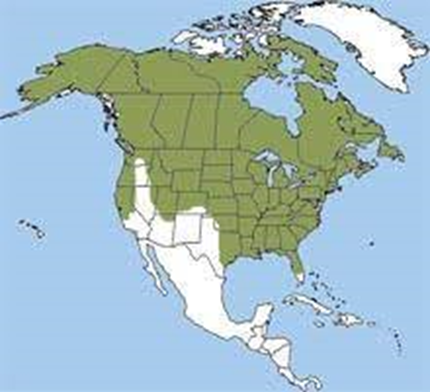
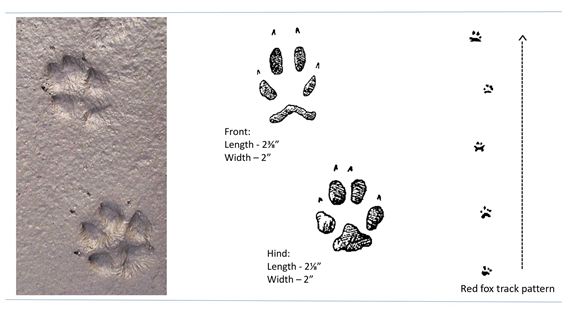
Identification
- The red fox is dog-like in appearance, with an elongated pointed muzzle and large pointed ears that are usually erect and forward. They have thick, soft body hair and a furry, bushy tail. Red foxes are colored with a light-orange coat, black legs, lighter-colored underfur and a white-tipped tail.